The experimental setup/testbed at ICCS offers a multi-access network environment tailored for the support of (multi-access) edge computing. The access network infrastructure consists of various small cells supporting 4G and 5G NR (particularly 3x 4G base stations and 2x 5G NSA cell cites), along with IEEE 802.11 (WiFi) access points and one Road Side Unit (RSU) offering ITS G5 communication capabilities tailored for the automotive sector.
The 4G/5G small cells are purely software-defined as they are driven by fully reconfigurable and open software defined radio (SDR) equipment i.e., USRP B210 and USRP N310 devices. Emphasis is given on edge computing capabilities with the integration of micro-data center infrastructure at each radio access point i.e., the 4G/5G small cells, the WiFi hotspots and the RSU, realized in the form of lightweight server capabilities (16 CPU cores, 32 GB RAM per access point). All radio access points are connected (via copper) to a core facility, which hosts the main volume of compute and storage resources. The core facility hosts a total computing power of 288 CPU cores and 92 GB of RAM. The core facility hosts:
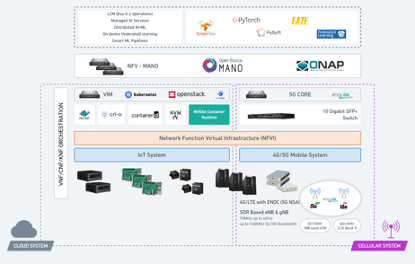
The experimental setup/testbed at ICCS offers a multi-access network environment tailored for the support of (multi-access) edge computing. The access network infrastructure consists of various small cells supporting 4G and 5G NR (particularly 3x 4G base stations and 2x 5G NSA cell cites), along with IEEE 802.11 (WiFi) access points and one Road Side Unit (RSU) offering ITS G5 communication capabilities tailored for the automotive sector. The 4G/5G small cells are purely software-defined as they are driven by fully reconfigurable and open software defined radio (SDR) equipment i.e., USRP B210 and USRP N310 devices. Emphasis is given on edge computing capabilities with the integration of micro-data center infrastructure at each radio access point i.e., the 4G/5G small cells, the WiFi hotspots and the RSU, realized in the form of lightweight server capabilities (16 CPU cores, 32 GB RAM per access point). All radio access points are connected (via copper) to a core facility, which hosts the main volume of compute and storage resources. The core facility hosts a total computing power of 288 CPU cores and 92 GB of RAM.
The core facility hosts:
(i) An LTE EPC (Open Air Interface) instance supporting 4G, as well as 5G Non-stand Alone (NSA) functionality; migration to 5G SA is currently ongoing.
(ii) An Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) Management and Orchestration (MANO) software platform including ETSI compliant and industry proven technologies such the OpenSourceMANO orchestrator; a full-fledged OpenStack instance realizing the Virtualized Infrastructure Manager (VIM)/controller functionality; as well as microservice based cloud native technologies (certified CaaS — Container as a service) based on Kubernetes, including also lightweight implementations such as microk8s and k3s, to support diverse application requirements tailored to constrained IoT systems (e.g., CPU, storage, battery, networking).
(iii) The Network Functions Virtualization Infrastructure (NFVI) for the realization of NFVs, in the form of Virtual Machines or Containers (i.e., through orchestration of VNFs/CNFs/KNFs), hosted on legacy x86 systems and ARM based architectures, exploiting the resources of the NFVI nodes including CPUs, GPUs, Storage and Networking. It is noted that on a MANO level, the overall testbed architecture includes all Points-of-Presence (PoP) namely the core facility compute nodes as well as the aforementioned edge computing PoPs. For the latter, additional management frameworks are currently under assessment, including LF Edge solutions e.g., EdgeXFoundry.
Completing the overall experimental infrastructure, several UEs of various types are available e.g., mobile phones of various vendors, laptops equipped with appropriate dongles, Software-defined UEs based on SDN platforms. All types of UEs have embedded USIMs, suitable for authentication to EPC.
The following figure illustrates a set of services and platforms (including software and hardware components) supported by the ICCS 5G testbed including AI/ML pipelines, orchestration and cellular connectivity.

